Nanotechnology and corrosion protection:
the era of graphene oxide
Corrosion is defined as the gradual deterioration of metallic materials and their properties, and occurs when the metal reacts with the surrounding environment to form rust or another chemical compound. In general, atmospheric air, humidity, rain, and aqueous solutions (chemical products) are the environments that are most frequently associated with corrosion problems.
Nowadays, corrosion damage is one of the most important problems to face for many industries in the world. It is estimated that corrosion causes economic losses of 3.4% of world GDP (about 2.5 billion dollars per year). However, there are three industries whose corrosion impact is more frequent and riskier for their processes: the chemical industry, the shipbuilding industry and the construction industry.
In the chemical industry, the use of chemical products is paramount within its operations, so equipment and machinery are in direct and constant contact with chemical substances, increasing maintenance and/or repair costs, affecting the industry budget and their production. In the case of the naval industry, humidity and salt are the main factors that contribute to the corrosion process and, consequently, the deterioration and affectation of its facilities, ships, containers and even merchandise. On the other hand, in the construction industry, both the machinery and the construction areas themselves can be affected by corrosion due to their exposure to the environment. Corrosion causes the metallic assets to weaken, generating mechanical failures, putting the work at risk.

Anticorrosive coatings are regularly used for protection against corrosion, humidity and fouling of installations, machinery and equipment. At a commercial level, there is a wide variety of anticorrosive coatings based on different additives and resins, their efficiency is generally associated with an increase in cost. However, the coatings still have low thermal and corrosion resistance and especially limited chemical resistance.
Graphene is currently the most revolutionary nanotechnological additive in the coatings and paints industry. The incorporation of graphene as an additive in coatings produces coatings with extraordinary protection against corrosion. Graphene creates pathways that are very tortuous, preventing water and oxygen molecules and/or chemical agents from diffusing to the surface of metal-based materials, resulting in metal protection against oxidation and corrosion. corrosion (Fig. 1).
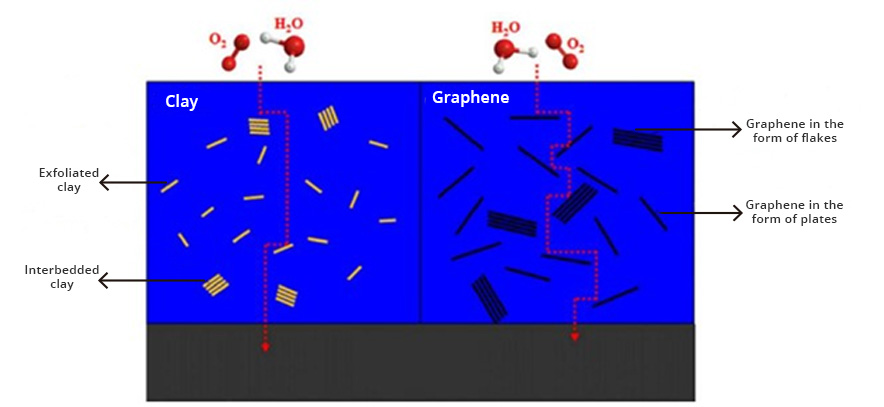
Graphene coatings provide many performance and anti-corrosion benefits, including:
- Higher performance than existing coating technologies on the market today.
- Fewer applied coating layers are required for greater benefits
- Zinc reduction in formulations
- Chemical resistance
Graphene and graphene oxide-enhanced anticorrosive coatings will replace traditional zinc-based coatings, which have several drawbacks, such as short life, high content of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), slow curing, high cost, sedimentation in storage.
Currently Energeia – Graphenemex®, a leading Mexican company in Latin America in research and production of graphene materials for the development of industrial applications, through its Graphenergy line, has launched a wide range of nanotechnological coatings with graphene. These coatings offer high anticorrosive protection, extraordinary chemical resistance, high wear resistance, resistance to UV rays, impermeability and greater adherence, in order to improve the useful life of any surface or installation and reduce maintenance costs.
References
- Chang, C.-H. et al. Novel Anticorrosion Coatings Prepared from Polyaniline/Graphene Composites. Carbon N. Y. 50, 5044–5051 (2012).
- Fengjuan Xiao, Chen Qian, et al., et al., Progress in Organic Coatings, 125, 79-88 (2018); doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2018.08.027
- Chaudhry, A. U., Mittal, V. & Mishra, B. Inhibition and Promotion of Electrochemical Reactions by Graphene in Organic Coatings. RSC Adv. 5, 80365–80368 (2015).
- Zhen, Z. & Zhu, H. Graphene: Fabrication, Characterizations, Properties and Applications. Graphene (Academic Press, 2018).

