GRAPHENE
The material of the future, today
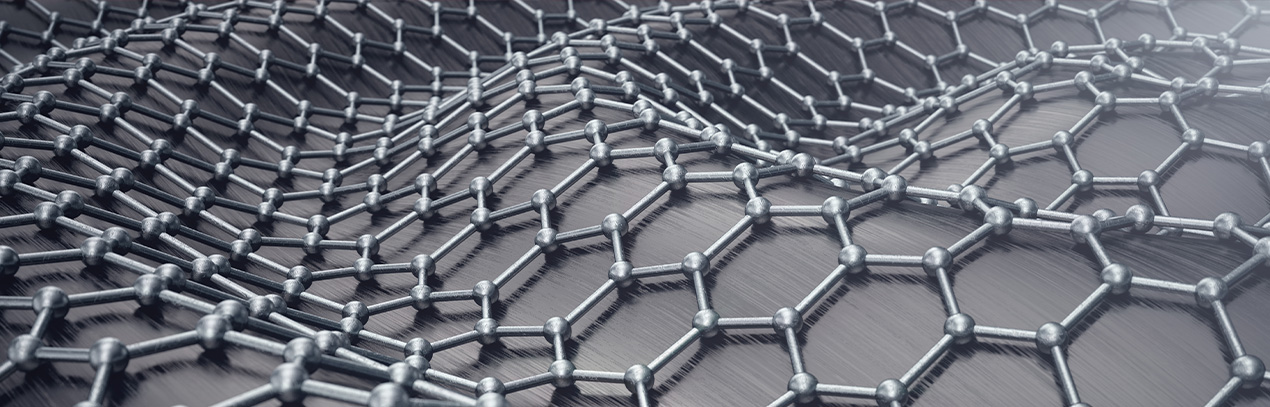
Graphene, a revolutionary nanomaterial, represents the forefront of innovation. Composed of layers of carbon arranged in a hexagonal structure, graphene is extraordinarily strong and lightweight, promising to transform industries with its versatility and unique properties.
History
2004
Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov isolate and characterize graphene for the first time at the University of Manchester, earning them the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010.

2006
A method is developed to produce graphene sheets on a large scale using adhesive tape, known as the exfoliation method.
2008
Researchers demonstrate graphene’s exceptional thermal conduction properties.

2010
The European Union launches the Graphene Flagship Project, a multimillion-dollar initiative to boost research and application of graphene in various industries.

2011
Extraordinary mechanical properties of graphene are discovered, proving to be the strongest known material.

2013
Initial research on the antibacterial properties of graphene begins.
2014
Researchers develop a method to print flexible electronic circuits using graphene inks.

2016
Significant advances are made in utilizing graphene in lithium-ion batteries, opening new possibilities in energy storage.

2018
Graphene synthesis in a liquid phase is achieved, facilitating its application in a variety of materials and products.

2020
Graphene is used in medical applications, such as sensors for disease detection and in the creation of biocompatible materials.

2022
Companies begin to use graphene in consumer products, such as sportswear and electronic devices.

2023
Significant progress is made in the mass production and affordability of graphene, accelerating its integration into various industries.

2024
India launches the Graphene Innovation Center, aiming to create a start-up ecosystem in the field of graphene and 2D materials.

Properties

It is 200 times stronger than steel and is 5 times lighter than aluminum.

It is highly impermeable, even to hydrogen and helium.

Depending on the type of graphene material, it can conduct electricity or be insulating.

It is biocompatible.

It has antimicrobial properties.

It is resistant to UV rays and corrosion.

It can be functionalized to create different graphene materials for each application.
Graphenemex
More Information
LATEST NEWS ON GRAPHENE
Graphene and Bioplastics: Innovation for Enhanced Sustainability
Biocompatibility and Biodegradability of Graphene: Advances and Scientific Evidence
Graphene, the differentiating material for the use of solar energy
Graphene Functionalization
Graphene Aerogels
Graphene
Featured links on graphene
 Engage with Graphene
Engage with Graphene
 The Graphene Experts
The Graphene Experts
 Graphene Flagship
Graphene Flagship
 Graphene Update
Graphene Update