Graphene in protection
against electromagnetic radiation
The development of communication technology together with electronic devices has generated great concern regarding the electromagnetic radiation emitted by these technologies.
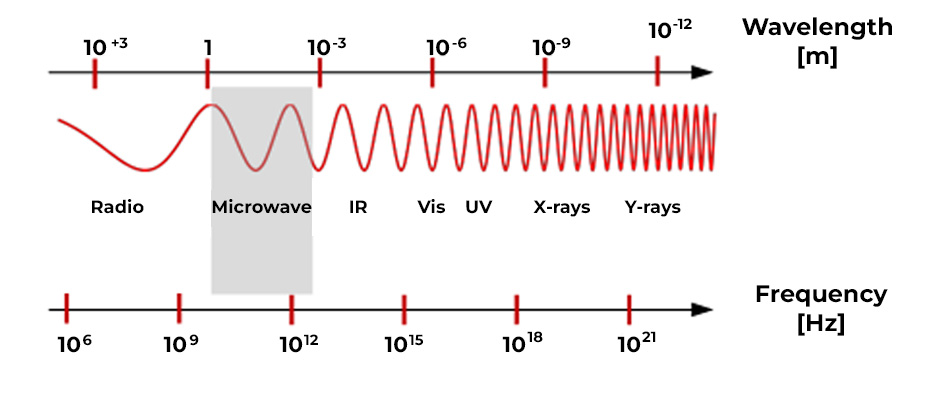
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of electromagnetic field, that is, a combination of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which propagates through space carrying energy from one place to another. Electromagnetic radiation can manifest itself in various ways, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays or gamma rays and correspond to different wavelengths, ranging from kilometers (radio waves) to the order of picometers (gamma rays). The full range of wavelengths is what is called the electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 1.).
Electromagnetic radiation can be high frequency (radiation from mobile and wireless telephones, radio frequencies, TV waves, microwaves, radar, satellite signals, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) and low frequency (fields generated by cables or electrical consumers).
Heat and electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation) are unavoidable by-products in electronic devices, especially those that operate at high frequencies. As electronic devices get smaller, they operate at higher and higher frequencies, generating even more heat and electromagnetic waves.
High frequency electromagnetic radiation not only degrades the devices themselves (producing heat), but also tends to interfere with neighboring electronic devices and most importantly, it has an adverse effect on human health as it can cause many diseases, such as leukemia, miscarriages, and brain cancer.
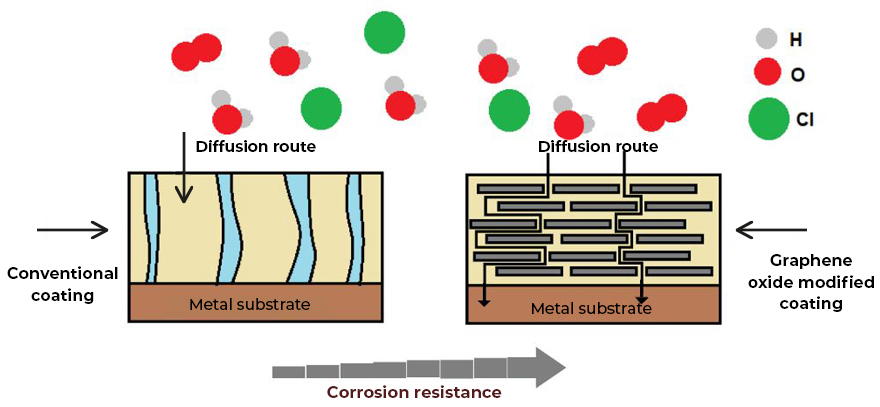
Therefore, the blocking or protection (shielding) against electromagnetic radiation could be one of the solutions to minimize health risks and for the protection of electronic equipment and/or devices. Metals are natural electromagnetic blocking materials, capable of reflecting electromagnetic waves due to their free electrons, which explains their high electrical conductivity and low penetration depth. However, their heavy weight, cost and the susceptibility of metals to corrosion make their use limited if not impossible.
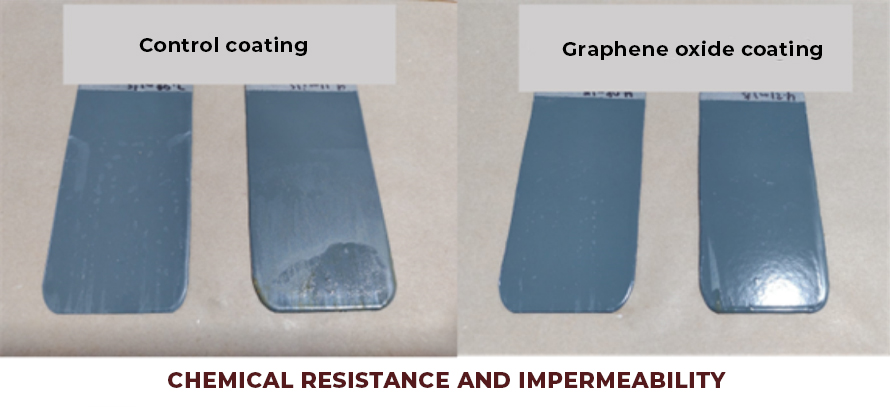
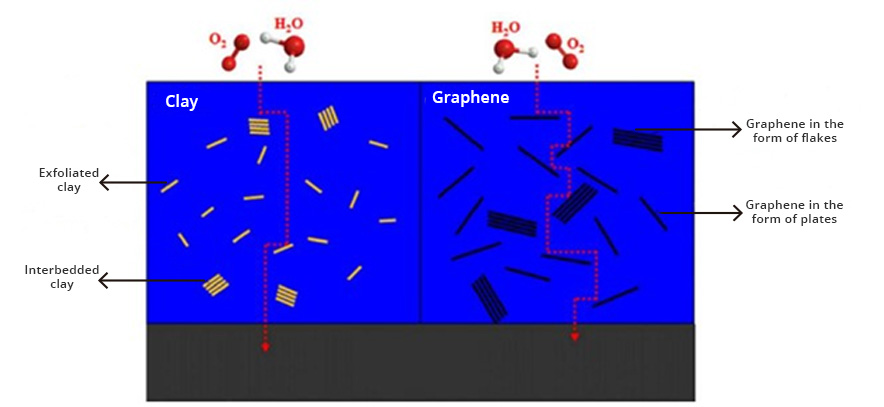
The use of conductive coatings or paints to block electromagnetic radiation is the most viable option to solve the problem. Graphene is currently the most revolutionary nanotechnological additive in the coatings industry. Because graphene has extraordinary properties, which include high electrical conductivity, high thermal conductivity, and mechanical resistance. In addition, it possesses other distinctive properties, including gas impermeability, chemical resistance, antibacterial potential, and large surface area.
The electrical conduction capacity and thermal conductivity of graphene can be exploited in the formulation of shielding coatings against EM radiation, since graphene forms a continuous network along the surface of the coating, creating homogeneous films that block radiation. electromagnetic radiation while dissipating excess heat. In recent studies, it has been reported that the incorporation of carbon-based nanostructures, such as graphene in coatings or paints, allows the development of coatings with high electrical conductivity for shielding or protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI). The way to act with respect to high frequency electromagnetic waves is by refraction. Electromagnetic waves will bounce (reflect) off the treated surface similar to the effect of a mirror with respect to light (See Fig. 2). The barrier-effect in the propagation could be attributed to the contribution coming from the reflection capacity, the absorption and multiple internal reflections. The shielding efficiency increases with the addition of a higher concentration of graphene in the polymeric matrix of the coating. These graphene coatings can block more than 99.98% of high-frequency electromagnetic radiation.
Taken from Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5. 1800558
These coatings against electromagnetic radiation can act for both high frequency and low frequency, with an excellent quality of attenuation (decrease in intensity of signals or electric waves) of up to 38 dB, with one hand, and 47 dB if applied. two hands.
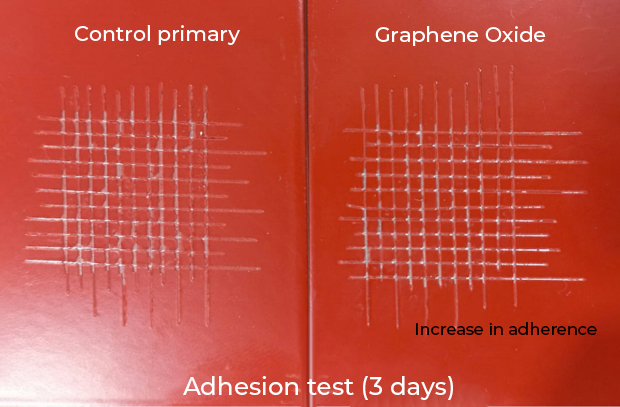
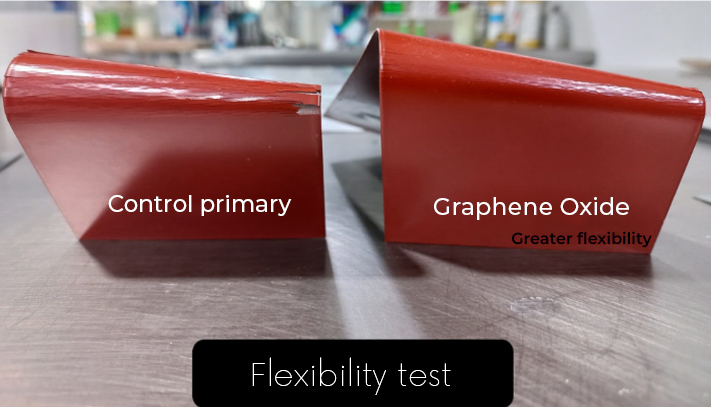
Energeia – Graphenemex®, a leading Mexican company in Latin America in research and production of graphene materials for the development of applications at an industrial level, through its Graphenergy line, is constantly researching and developing new multifunctional coatings and currently has for sale a wide range of nanotechnological coatings with graphene. Shielding coatings against electromagnetic radiation are currently being developed and evaluated. Coatings with high electrical conductivity, to reduce high and low frequency electrical fields respectively. These coatings will also offer anticorrosive and antimicrobial protection. In addition, to provide high resistance to wear, resistance to UV rays, impermeability and extraordinary adhesion.
Referencias
- Suneel Kumar Srivastava, Kunal Manna, Recent advancements in the electromagnetic interference shielding performance of nanostructured materials and their nanocomposites: a review, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 10.1039/D1TA09522F, 10, 14, (7431-7496), (2022).
- Kargar, F., Barani, Z., Balinskiy, M., Magana, A. S., Lewis, J. S., Balandin, A. A., Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800558.
- Seul Ki Hong et al 2012 Nanotechnology 23 455704.
- Lekshmi Omana, Anoop Chandran*, Reenu Elizabeth John, Runcy Wilson. Recent Advances in Polymer Nanocomposites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding: A Review. Omega 2022, 7, 30, 25921–25947